How SSL Works: A Simple Guide
If you've ever noticed the little padlock icon in your browser or seen "https://" in a website URL, you've encountered SSL (Secure Sockets Layer). But what exactly is it, and how does it keep your data safe? Let’s break it down in a clear, beginner-friendly way, covering what an SSL certificate is, the key players involved, and how the whole process works.
What is an SSL Certificate?
An SSL certificate is a digitally signed document that binds a public key to an identity, typically a specific domain name (e.g.,aiverseapp.site). Think of it like a digital passport for a website—it verifies that the site is legit and enables secure, encrypted communication between your browser and the server.
The certificate contains:
- The domain name it’s issued for.
- A public key used for encryption.
- Details about the issuer (a trusted Certificate Authority, or CA, like Cloudflare).
- A digital signature to prove its authenticity.
Key Players in the SSL Process
To understand SSL, you need to know the main components and parties involved:- Origin Server\
- Edge Server\
- You use Cloudflare’s DNS and point your domain to Cloudflare’s nameservers.
- These nameservers define how domain operations work, like redirecting
www.domain.comto your service or pointingsubdomain.domain.comto a specific server.
- Domain Name Server (DNS Provider)\
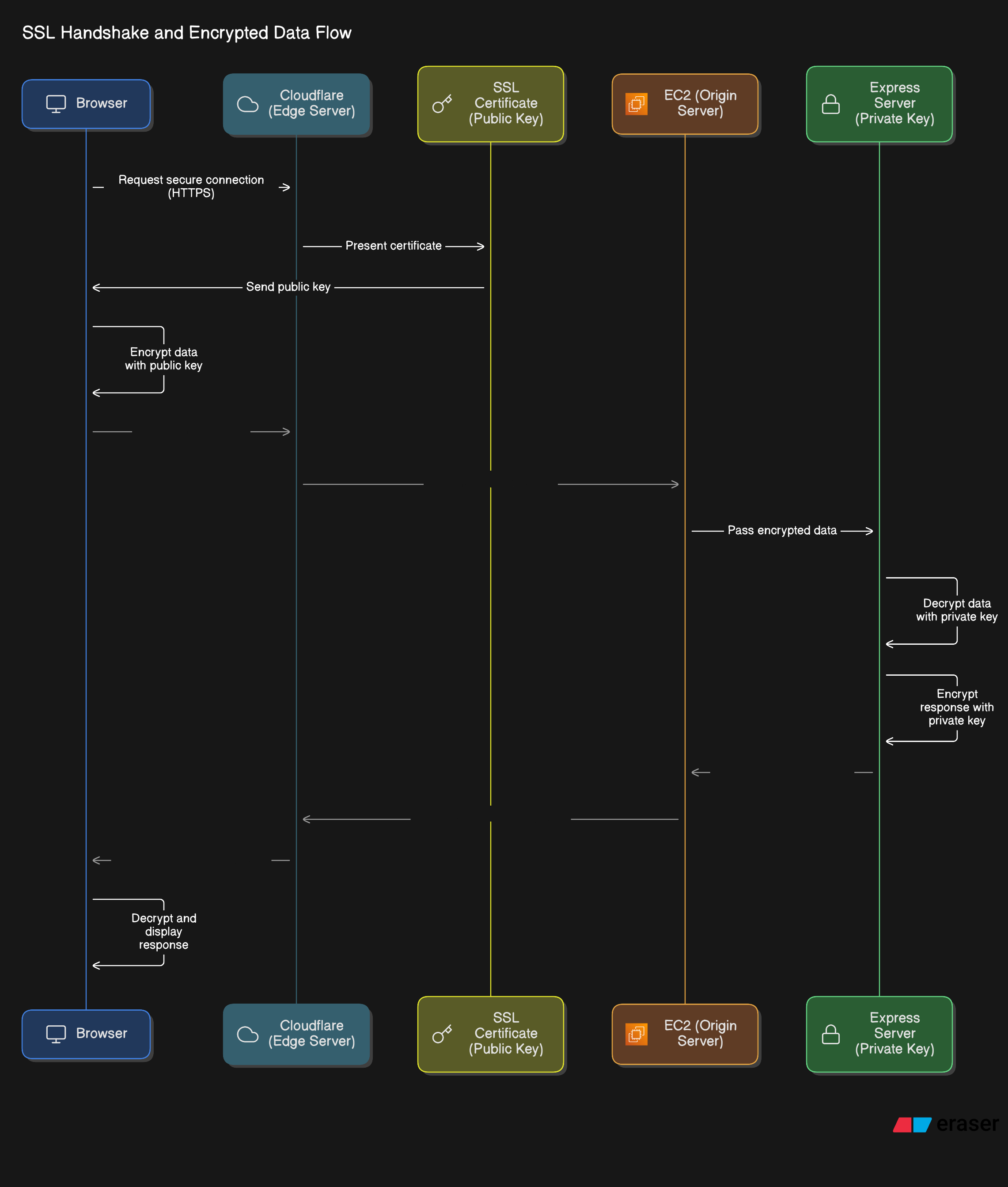
How Does SSL Work?
SSL ties a specific domain to the encryption process, ensuring data sent between your browser and the server is secure. It uses public key (asymmetric) encryption, which is the backbone of this system. Let’s break it down step by step.Step 1: Understanding Public Key Encryption
- Public Key: Included in the SSL certificate, this key is shared with everyone. Anyone can use it to encrypt data.
- Private Key: Kept secret by the server, this key is used to decrypt data encrypted with the public key.
- Imagine you’re sending a locked box to a friend. The public key is like a padlock anyone can snap shut, but only your friend has the private key to unlock it.
- In SSL, your browser uses the public key (from the SSL certificate) to encrypt data, and only the server with the private key can decrypt it.
Step 2: The SSL Workflow
Let’s walk through what happens when you visitaiverseapp.site, using Cloudflare as the edge server and an EC2 instance as the origin server:
- Your Browser Requests the Website\
aiverseapp.site into your browser, the request goes to Cloudflare’s edge server (since the domain’s nameservers point to Cloudflare).
- Cloudflare Presents the SSL Certificate\
aiverseapp.site (and possibly *.aiverseapp.site for subdomains). This certificate includes the public key. Your browser verifies the certificate with the issuing Certificate Authority to ensure it’s valid.
- Encryption Begins\
- Cloudflare Forwards the Request\
- The Origin Server Decrypts\
- Secure Communication Continues\
Why Cloudflare?
Cloudflare simplifies SSL by acting as a middleman. It provides free SSL certificates, handles encryption at the edge, and ensures secure communication between the edge and origin servers. For example, with a wildcard certificate (*.aiverseapp.site), you can secure multiple subdomains without needing separate certificates.
Why SSL Matters
SSL ensures:- Data Privacy: Sensitive information (like passwords) is encrypted.
- Data Integrity: Data can’t be tampered with during transit.
- Trust: Users see the padlock and know your site is legit.
Tags
#SSL#HTTPS#Encryption#Digital Certificates#SSL Handshake#Web Security#Online Privacy